Decoding Flavor Fusion: The Microbial Symphony of Ingredients and Cooking Temperatures in Stir-Fry
Stir-fry is a culinary art that beautifully showcases the concept of flavor fusion techniques. The combination of various ingredients, alongside their cooking temperatures, creates delicious outcomes through intricate microbial interactions. In this extensive guide, we will explore the science behind stir-frying, the roles of microbial activity, and how different cooking temperatures can enhance flavor fusion.
The Basics of Stir-Frying
Stir-frying is a traditional cooking technique originating from Asia, primarily China. It involves cooking food quickly at high heat in a wok or a large frying pan. This cooking method utilizes minimal oil but maximizes flavor through rapid cooking. Understanding the basics is fundamental to unlocking the deeper complexities of flavor fusion techniques.
Key Ingredients in Stir-Fry
To create an exceptional stir-fry, the choice of ingredients is critical. Here are the main components:
- Proteins: Common choices include chicken, beef, shrimp, and tofu.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, bell peppers, snap peas, and carrots are popular picks.
- Flavoring Agents: Soy sauce, oyster sauce, garlic, ginger, and sesame oil are frequently used to enhance taste.
- Starches: Rice or noodles often accompanies stir-fried dishes.
The Science of Ingredients
The diverse array of ingredients plays a crucial role in flavor fusion techniques. Each component contributes varying levels of taste and aroma due to its unique chemical makeup. Let’s delve into how different ingredients impart their flavors:
Proteins and Their Flavor Profile
Proteins are essential in stir-fry recipes, providing much of the dish’s heartiness and flavor. The Maillard reaction occurs when proteins are exposed to high heat during cooking, resulting in browning and producing complex flavors. The following proteins are commonly recognized for their flavor-enhancing properties:
- Chicken: Mild flavor absorbs seasonings well.
- Beef: Rich umami notes enhance a savory profile.
- Shrimp: Sweet and oceanic flavors complemented by heat.
- Tofu: Neutral taste that transforms with other mingled flavors.
Vegetables Contribution to Flavor
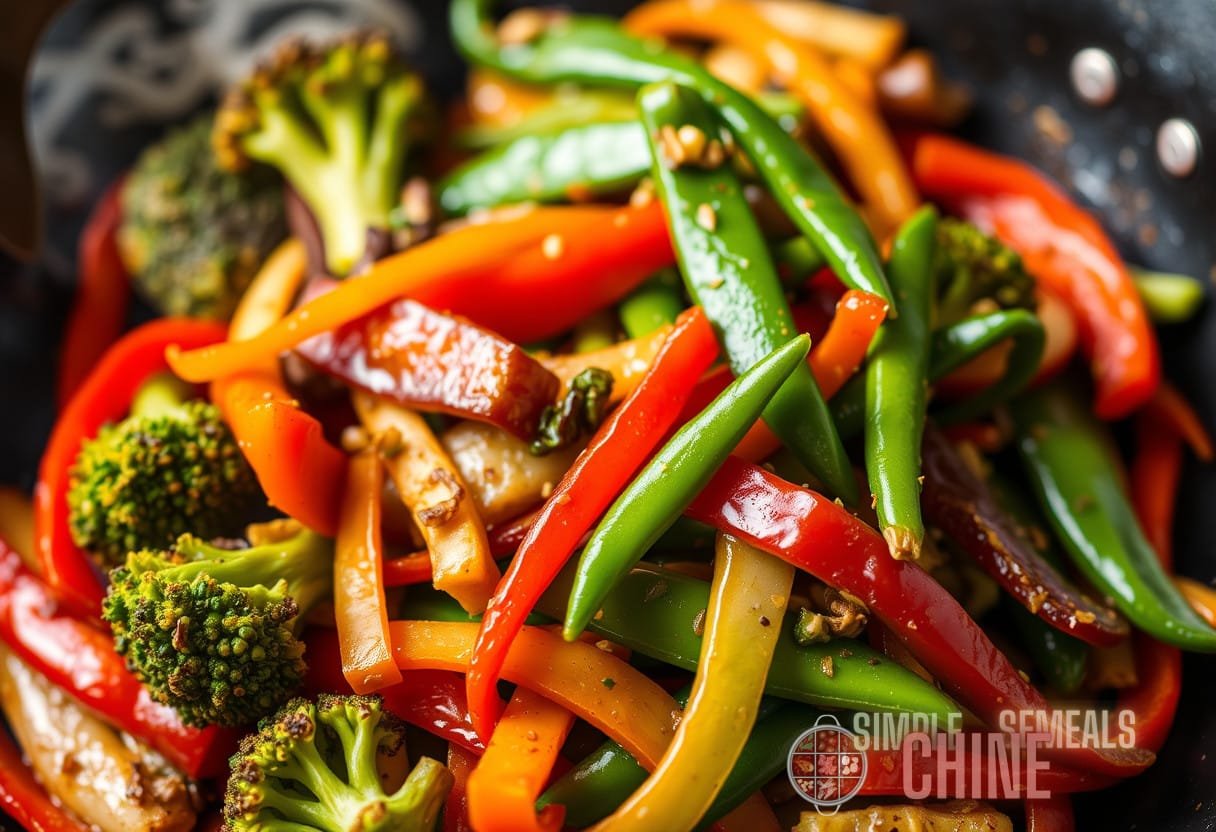

Vegetables not only provide nutritional benefits but also contribute unique aromas and textures to stir-fry dishes. Their natural sugars caramelize at high temperatures, leading to delightful flavor fusions:
- Broccoli: Bitter and nutty flavors enhance through roasting.
- Bell Peppers: Sweetness elevates the overall dish while providing color.
- Snap Peas: Crisp and slightly sweet, these are best cooked quickly for texture.
Understanding the Role of Microbial Activity
Microbial activity, primarily through fermentation, has a significant influence on flavor development. The presence of bacteria and yeast in some ingredients is crucial for enhancing the depth of flavors. Several fermented elements are prevalent in stir-fries:
- Fermented Sauces: Ingredients like soy sauce and miso enhance the umami flavor.
- Fermented Vegetables: Items such as kimchi can add tanginess and crunch.
The Process of Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that converts sugar to acids, gases, or alcohol using microorganisms such as bacteria and yeast. The results of fermentation change the flavor profile of ingredients, creating a synergy that adds complexity to stir-fry dishes. For example, the fermentation process in making soy sauce results in numerous compounds, making it a key flavor-packed ingredient in many stir-fry recipes.
Real-World Applications of Microbial Flavor Fusion
Restaurants around the world utilize flavor fusion techniques inspired by microbial activity. For instance, in a trendy Asian fusion dining establishment, chefs may fuse Thai-style fish sauce with traditional soy sauce to amplify savoriness in stir-fries, revealing flavors not previously considered. Another example can be seen in Korean stir-fry recipes that routinely incorporate kimchi, creating unique taste profiles that signify gourmet cooking influenced by decades of culinary wisdom.
Temperature and Its Impact on Flavor Fusion Techniques
Temperature control is critical in executing a successful stir-fry. Cooking at high heat leads to different flavor outcomes compared to lower temperatures. Here’s how temperature influences cooking:
- High Temperature Cooking: This method fosters quick cooking, promoting the Maillard reaction and evaporating moisture, concentrating flavors. It ensures vegetables remain crisp but tender.
- Low Temperature Cooking: While generally not recommended for traditional stir-frying, lower temperatures can coax out different flavor compounds, perfect for stewing or braising.
Flavor Pairing in Stir-Fry
Pairing ingredients wisely is essential to produce harmonious flavors in stir-fry dishes. Here’s a guide to coupling elements for optimal taste:
- Sweet and Spicy: Combine bell peppers and chili paste for a balanced contrast.
- Savory and Sour: Pair soy sauce with vinegar to stimulate taste buds.
- Earthy and Umami: Integrate mushrooms with sauces rich in umami notes.
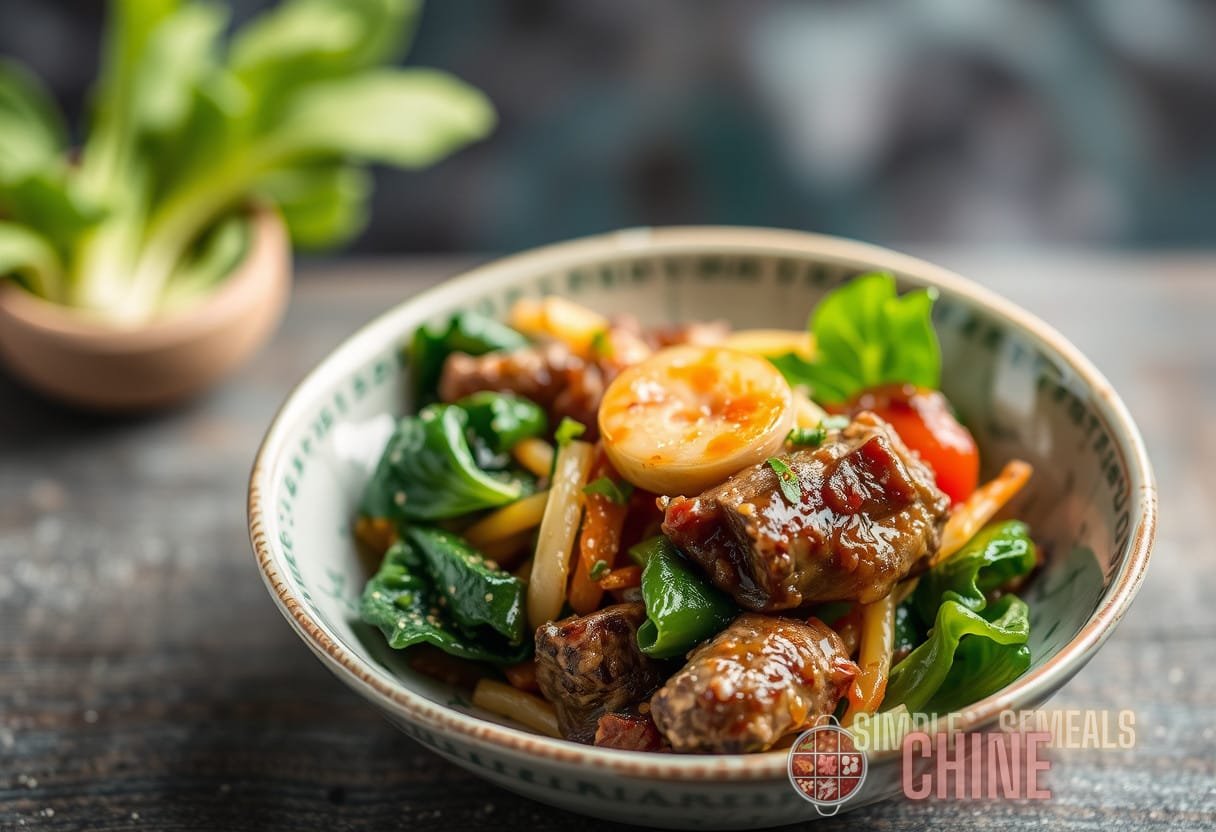

Case Study: A Fusion Stir-Fry Recipe
Consider creating a fusion stir-fry featuring:
- Protein: Beef or tempeh for a hearty base.
- Vegetables: A medley including bok choy, bell peppers, and zucchini.
- Flavoring Agent: A mixture of soy sauce, ginger, and a touch of honey.
Step-by-Step Cooking Guide
Follow these easy steps to craft a perfect fusion stir-fry:
- Begin by prepping ingredients, cutting vegetables and proteins into even sizes to ensure uniform cooking.
- Heat a wok until smoking. Add a small amount of oil, and when it shimmers, introduce the protein.
- Once proteins are nearly cooked, add vegetables in the order of hardness (i.e., carrots first, followed by softer vegetables like zucchini).
- Pour the sauce mixture over the dish, allow it to bubble, and then stir-fry everything together.
- When vegetables are bright but tender, remove from heat and serve immediately on a bed of rice or noodles.
Tips for Perfecting Your Stir-Fry
To take your stir-fry to the next level, consider these expert tips:
- Use a wok for even heat distribution.
- Prepare all ingredients in advance to maintain a quick cooking time.
- Experiment with flavor fusion techniques by trying out new sauces or spices.
- Stir-fry in batches if cooking for several people to maintain high heat.
Conclusion: The Symphony of Stir-Fry
Understanding the microbial symphony of ingredients and cooking temperatures is essential in mastering the art of stir-fry. By delving into the realms of flavor fusion techniques, you can create dishes that are not only delicious but also a celebration of diverse culinary traditions.
For additional insights on stir-fry recipes and ideas, explore our detailed guide to seasoning techniques here or discover unique stir-fry variations here.